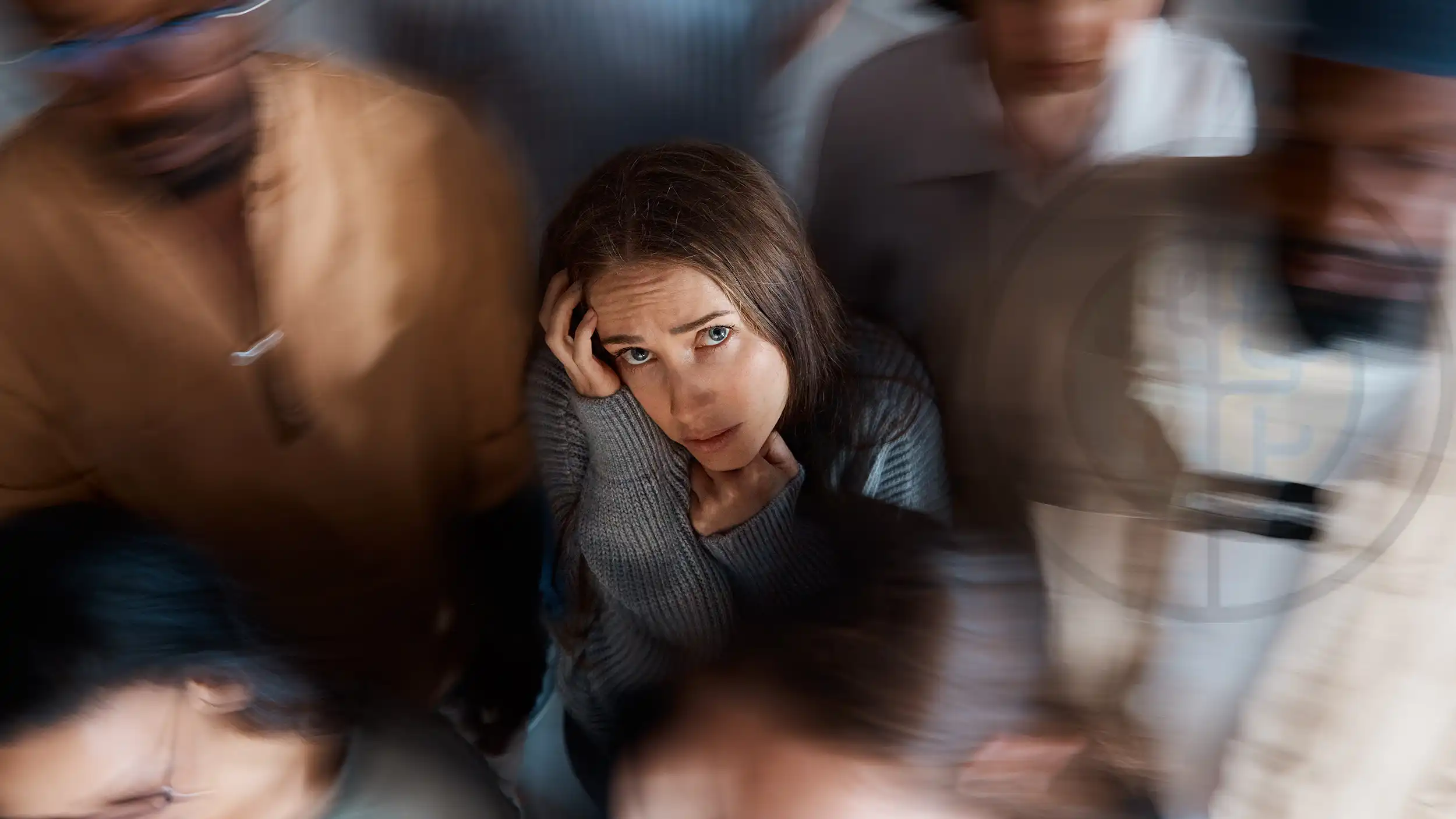

Agoraphobia
Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder that causes extreme fear and avoidance of places or situations in which the person may experience a state of panic or the feeling of being trapped, with no way out or in extreme embarrassment.
What is agoraphobia
The word derives from the combination of the Greek words αγορά (square) and φοβία (fear) and recalls the image of the market square, a chaotic and crowded place par excellence, from which it can be complicated to extricate oneself in case of need or discomfort.
Agoraphobia is an anxiety disorder that involves extreme fear and/or avoidance of places or situations in which the person may experience a state of panic or the feeling of being trapped, helpless or in extreme embarrassment.
Sufferers often fear being in crowds, standing in queues, entering supermarkets and travelling by car or public transport.
Anxiety is caused by the fear of not having an escape route or of not being able to get help if the discomfort becomes too intense.
Many people develop this disorder after experiencing one or more panic attacks. The experience causes them to worry intensely about the possibility of future attacks (fear of fear) and to avoid situations in which they believe they could get so sick again.
Most of the time, these people identify certain 'safe places' (such as home, immediate surroundings or familiar/familiar areas) beyond which, any movement causes a sudden increase in anxiety. Often, the company of a trusted person becomes necessary in order to be able to move.
Symptoms of agoraphobia
Those suffering from agoraphobia may avoid some of the following situations or activities:
- Being far from home
- Going anywhere without being accompanied by a trusted person
- Physical fatigue (because it is believed to stimulate a panic attack or a sense of malaise)
- Going to places where it is not easy to find an escape route (restaurants, theatres, shops, public transport)
- Driving
- Places where it might be embarrassing to have a panic attack or feel ill
How can we help you?
Exposure-based cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT) is the treatment of choice for agoraphobia.
We are all aware that to overcome a fear it is necessary to face it, but for those who have suffered from agoraphobia for years, the mere idea of doing so becomes a source of anxiety.
Before teaching the patient to face the feared situations in vivo, i.e. in reality, systematic desensitisation is frequently employed, a technique developed in the late 1950s by Joseph Wolpe to decondition people suffering from phobias (Panic attacks. How to get out of them. The power of Cognitive Behavioural Therapy. E. Rolla, 2017, IW editions).
La systematic desensitisation consists of confronting anxiety-provoking situations and thoughts, in imagination, by adopting relaxation techniques (or other strategies incompatible with fear), in order to alleviate the anxiety response.
After the work in imagination, the therapist, acting as a role model, accompanies the patient to gradually confront the feared stimuli in reality.
La in vivo exposure therapyIt aims, therefore, to encourage individuals to deal with anxiety-provoking situations (both in reality and in imagination) without avoiding them and by learning to tolerate the anxiety they arouse.